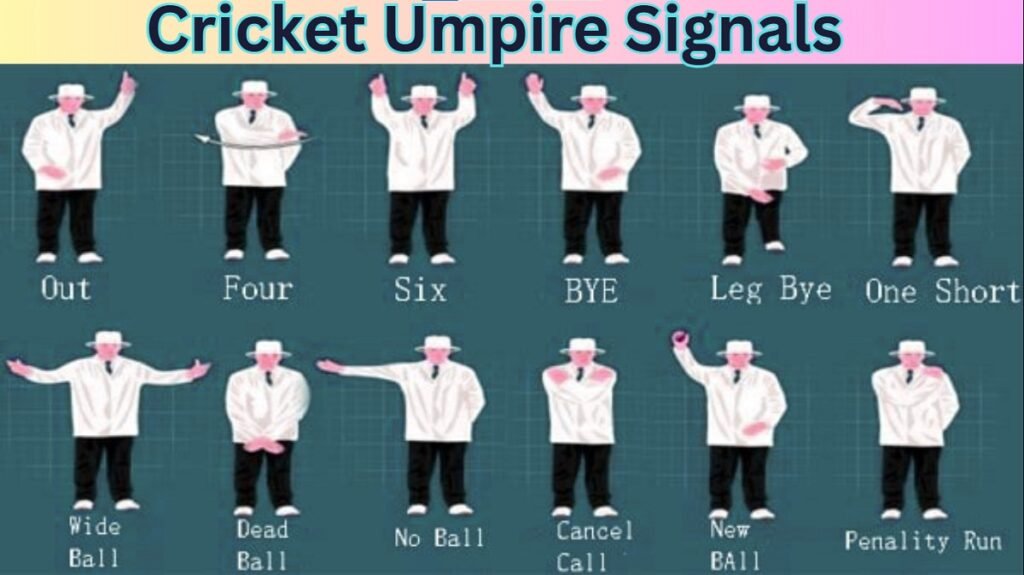
Cricket Umpire Signals
Cricket is a game of passion, precision, and regulations. While batters hit glorious shots and bowlers deliver magical deliveries, there’s one institution that ensures the clean strolling of the in shape — the umpires. Their function is going a ways beyond giving gamers out or no longer out. They communicate crucial decisions using a fixed of standardized hand indicators, which are universally recognized across all formats of cricket.
Whether you’re a fan looking the game or a player on the sphere, know-how these indicators allows you observe the float of the fit more intently. In this specific article, we’ll cover each cricket umpire sign, its that means, rule reference, and motive, with the assist of dependent causes and tables.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to Umpire Signals in Cricket
Cricket umpires are accountable for imposing the guidelines of the game. However, since cricket is a massive-area game with a massive target audience, umpires want a visual manner to communicate their decisions to players, scorers, and spectators.
That’s in which umpire hand signals are available. These gestures are clear, easy, and across the world standardized by the Marylebone Cricket Club (MCC) and the International Cricket Council (ICC).
Every sign corresponds to a specific rule — whether or not it’s for scoring, a dismissal, or an unlawful transport.
2. Role of Umpires in Cricket
Umpires in cricket are the on-discipline judges. Typically, there are on-field umpires:
- Main umpire (standing on the bowler’s end)
- Square leg umpire (status close to the leg aspect at a 90° perspective)
Additionally, in international matches, there may be a third umpire (TV umpire) and a fourth umpire to assist with off-discipline decisions.
Their roles include:
- Making choices on dismissals (out/no longer out)
- Signaling barriers and extras
- Ensuring truthful play and adherence to regulations
- Managing time and over fees
- Collaborating with era for opinions
3. Types of Cricket Umpire Signals
Umpire signals in cricket are divided into several kinds relying on the character of the decision:
| Category | Examples | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Scoring Signals | Four, Six, Leg Bye, Bye | To indicate runs scored |
| Illegal Delivery Signals | No Ball, Wide Ball | To identify unfair deliveries |
| Dismissal Signals | Out, Third Umpire Review | To indicate wickets |
| Administrative Signals | Drinks Break, Dead Ball | To manage the game flow |
4. Full List of Cricket Umpire Signals with Meaning
Below is a comprehensive list of all cricket umpire indicators with their meanings and factors.
| Signal Name | Gesture Description | Meaning / Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Out | Raise one index finger straight up | The batter is dismissed |
| Not Out | Shake head or no signal | Batter survives the appeal |
| Four Runs | Wave arm back and forth in front of chest | Ball crosses boundary after touching the ground |
| Six Runs | Raise both arms straight above head | Ball crosses boundary on full |
| No Ball | Extend one arm horizontally | Delivery is illegal; free hit next ball (in limited overs) |
| Wide Ball | Extend both arms horizontally | Ball is too wide for batter to reach |
| Bye | Raise one hand above head with an open palm | Runs scored without bat or body contact |
| Leg Bye | Touch raised knee, then raise arm | Runs scored off batter’s body |
| Dead Ball | Cross and uncross arms below waist | Ball is not in play |
| Penalty Runs | Touch shoulder with opposite hand | Five runs awarded to batting or fielding side |
| Revoke Decision (DRS) | Make a TV screen shape with both hands | Third umpire review referred |
| Short Run | Tap shoulder with one hand | One of the batters didn’t complete the run |
| Third Umpire Review Signal | TV screen gesture | Referring to video umpire for decision |
| Powerplay (in limited overs) | Circle arms above head | Indicates start of powerplay period |
| New Ball | Raise ball and point to umpire at bowler’s end | Used to signal change of ball after 80 overs in Tests |
| Drinks Break | Lift both hands towards mouth | Indicates an official drinks break |
| Change of Bowler | Point to the bowler and signal scorer | New bowler coming into attack |
| End of Over | Touch wrist or wave hand towards scorer | Indicates completion of over |
5. Signals for Runs and Boundaries
Scoring indicators are the maximum common ones visible in each cricket healthy. They inform scorers what number of runs had been brought and in what manner.
| Signal | Meaning | Points to Remember |
|---|---|---|
| Four Runs | Ball crosses boundary after touching the ground | 4 runs are added to batter’s score |
| Six Runs | Ball crosses boundary without touching ground | 6 runs added directly |
| Bye | Runs without bat or body | Counted as extras |
| Leg Bye | Runs off batter’s body | Counted as extras, not to batter’s total |
6. Signals for Dismissals
When a wicket falls, the umpire ought to make clean and assured indicators to speak the mode of dismissal.
| Dismissal Type | Umpire Signal | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Out (Any form) | Raise index finger straight up | Batter is declared out |
| Run Out (Referred) | TV screen gesture | Third umpire checks replay |
| LBW (Leg Before Wicket) | Raise index finger | Batter obstructed stumps with body |
| Caught | Raise index finger | Batter caught by fielder or keeper |
| Stumped | TV signal if referred | Keeper removes bails before batter returns |
| Hit Wicket | Raise index finger | Batter hit own stumps while playing |
7. Signals for Illegal Deliveries
Illegal deliveries consist of No-Ball and Wide Ball, each of which result in penalty runs.
| Signal | Gesture | Description |
|---|---|---|
| No Ball | One arm extended horizontally | Delivery is illegal (overstep, height, etc.) |
| Free Hit (after No Ball) | Circular arm motion | Next ball gives batter immunity from most dismissals |
| Wide Ball | Both arms extended horizontally | Ball is too wide or out of reach for the batter |
8. Signals for Match Control
Besides runs and wickets, umpires additionally manage sport administration thru signals.
| Signal | Meaning | When Used |
|---|---|---|
| Dead Ball | Ball is not in play | For interruptions or invalid deliveries |
| Drinks Break | Hands to mouth | Mid-session refresh break |
| End of Over | Tap wrist or wave | Over completed |
| Penalty Runs | Tap shoulder | 5 runs awarded for infringement |
| Change of Bowler | Point to new bowler | To update scorers |
9. Modern Technology & Third Umpire Role
In cutting-edge cricket, the 0.33 umpire performs an important position in reviewing near choices using DRS (Decision Review System).
The on-subject umpire makes use of a TV sign gesture (drawing a rectangle with hands) to refer the selection upstairs. The 1/3 umpire exams gradual-movement replays, ball-tracking, and hotspot technology before communicating the decision back.
Common DRS reviews consist of:
- Caught in the back of
- LBW selections
- Run outs
- Boundary checks (four or six)
- Fair or unfair catches
10. Interesting Facts About Cricket Umpire Signals
- Billy Bowden, the famous New Zealand umpire, became known for his particular, bent-finger “out” signal.
- Umpire signals are standardized global — from school fits to worldwide Tests.
- Some umpires customize gestures barely however inside allowed boundaries.
- The DRS (Decision Review System) was delivered in 2008, remodeling umpiring accuracy.
- Third umpire turned into first used in 1992 for the duration of an India vs South Africa Test match.
11. Importance of Learning Umpire Signals
For players, coaches, and fans alike, knowing umpire indicators is essential.
- Players: Must apprehend decisions immediately to respond correctly.
- Coaches: Use signals to analyze in shape situations.
- Fans: Helps observe the sport without observation.
- Scorers: Depend entirely on umpire signals for correct scoring.
12. FAQs on Cricket Umpire Signals
Q1. How many respectable umpire alerts are there in cricket?
👉 There are round 15–20 standardized signals, relying on healthy format and governing body.
Q2. What is the signal for a six in cricket?
👉 The umpire raises each fingers straight above the top.
Q3. What does a crossed arm sign mean?
👉 It manner Dead Ball — the ball is now not in play.
Q4. Who makes a decision if a ball is wide or not?
👉 The bowler’s stop umpire makes the call primarily based on batter’s stance and attain.
Q5. Is the 0.33 umpire sign mandatory?
👉 Only for selections requiring video evaluate, including run outs or disputed catches.
13. Conclusion
Cricket umpire signals are a language of the sport — silent but effective. Each gesture communicates critical records that continues gamers, scorers, and enthusiasts aligned. From signaling a six to declaring a batter out, umpires keep the rhythm of the fit in their palms.
In the modern-day generation of era, umpiring has come to be greater accurate, however the essence of those traditional hand alerts stays unchanged — a tribute to the rich way of life of cricket.